Use your Android XML themes in Jetpack Compose
A step-by-step guide on using your Android XML themes in Jetpack Compose, using Compose Unstyled.
This API is handy as you do not need to maintain two sources of truth (one being your XML themes and your Jetpack Compose themes) during the migration process.
This guide teaches you how to setup your Compose Unstyled theme using your Android XML theme, and use its values in your composables.
For the following guide, we will use this typical theme as a reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<style name="AppTheme" parent="@style/Theme.NoActionBar">
<item name="color_background">#FFFFFF</item>
<item name="color_onBackground">#262626</item>
<item name="color_primary">#3F51B5</item>
<item name="color_onPrimary">#FFFFFF</item>
<item name="textStyle_body">@style/Sans</item>
<item name="spacing_small">4dp</item>
<item name="spacing_medium">8dp</item>
<item name="spacing_large">12dp</item>
</style>
<style name="Sans">
<item name="android:textSize">18sp</item>
<item name="android:fontFamily">@font/inter</item>
</style>
<attr name="color_background" format="color"/>
<attr name="color_onBackground" format="color"/>
<attr name="color_primary" format="color"/>
<attr name="color_onPrimary" format="color"/>
<attr name="textStyle_body" format="reference"/>
<attr name="spacing_small" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="spacing_medium" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="spacing_large" format="dimension"/>
<!-- Base theme that removes the action bar and makes the activity full screen-->
<style name="Theme.NoActionBar" parent="">
<item name="android:windowFullscreen">true</item>
<item name="android:windowActionBar">false</item>
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
</style>
</resources>
Create your Compose theme
First off, let's create a Compose theme. It will be 'blank' for now. In the next steps it will be used as the bridge between XML and Compose.
Compose Unstyled comes with a theme builder function called buildTheme {}. It returns a @Composable theme
function that you can use to wrap your application content.
If you are coming from Material Compose, the result of buildTheme {} works the same way as Material's
MaterialTheme {} function.
Let's create a blank theme and use it to wrap the contents of our app:
import com.composeunstyled.Button
import com.composeunstyled.Text
import com.composeunstyled.theme.buildTheme
val AppTheme = buildTheme { }
@Composable
fun App() {
AppTheme {
Column(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text("Hello Styled World!")
Button(
onClick = { },
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 12.dp, vertical = 8.dp),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(100)
) {
Text("Click Me")
}
}
}
}
Did you notice that we use the Text and Button components? These components
are automatically styled
based off your current theme. You are not force to use them, but they make styling a breeze.
Use your XML colors in Compose
Now let's connect the XML world to the Jetpack Compose world.
Compose Unstyled comes with a Theme object, which is how you can reference values from the current theme. This is
similar to Material's MaterialTheme object, but in our case it's way more flexible.
Let's create a colors ThemeProperty and put some color ThemeTokens to it. We will use these tokens to populate
our theme and style our app:
val colors = ThemeProperty<Color>("colors")
val background = ThemeToken<Color>("background")
val onBackground = ThemeToken<Color>("onBackground")
val primary = ThemeToken<Color>("primary")
val onPrimary = ThemeToken<Color>("onPrimary")
We can now use them in our theme function to read the values of our XML theme.
Compose Unstyled comes with resolveThemeX() composable functions so that you can read your XML theme values:
val AppTheme = buildTheme {
// get a reference to the calling (themed) context
val context = LocalContext.current
// map your XML colors to Compose
properties[colors] = mapOf(
background to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_background),
onBackground to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onBackground),
primary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_primary),
onPrimary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onPrimary),
)
}
Note: Compose Unstyled does not inflate any XML themes for you. The
resolveThemeX()functions map the given context's theme attributes to Compose's. TheLocalContextreferences the context from which you will callAppThemefrom. For example, if you call it from your Activity'ssetContent {}function, it will inherit theandroid:themeof your AndroidManifest.xml file.
We can now use our XML theme colors directly in Compose.
To access them, use the Theme object like this:
@Composable
fun App() {
AppTheme {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Theme[colors][background]),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
ProvideContentColor(Theme[colors][onBackground]) {
Text("Hello Styled World!")
Button(
onClick = {},
backgroundColor = Theme[colors][primary],
contentColor = Theme[colors][onPrimary],
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 12.dp, vertical = 8.dp),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(100)
) {
Text("Click Me")
}
}
}
}
}
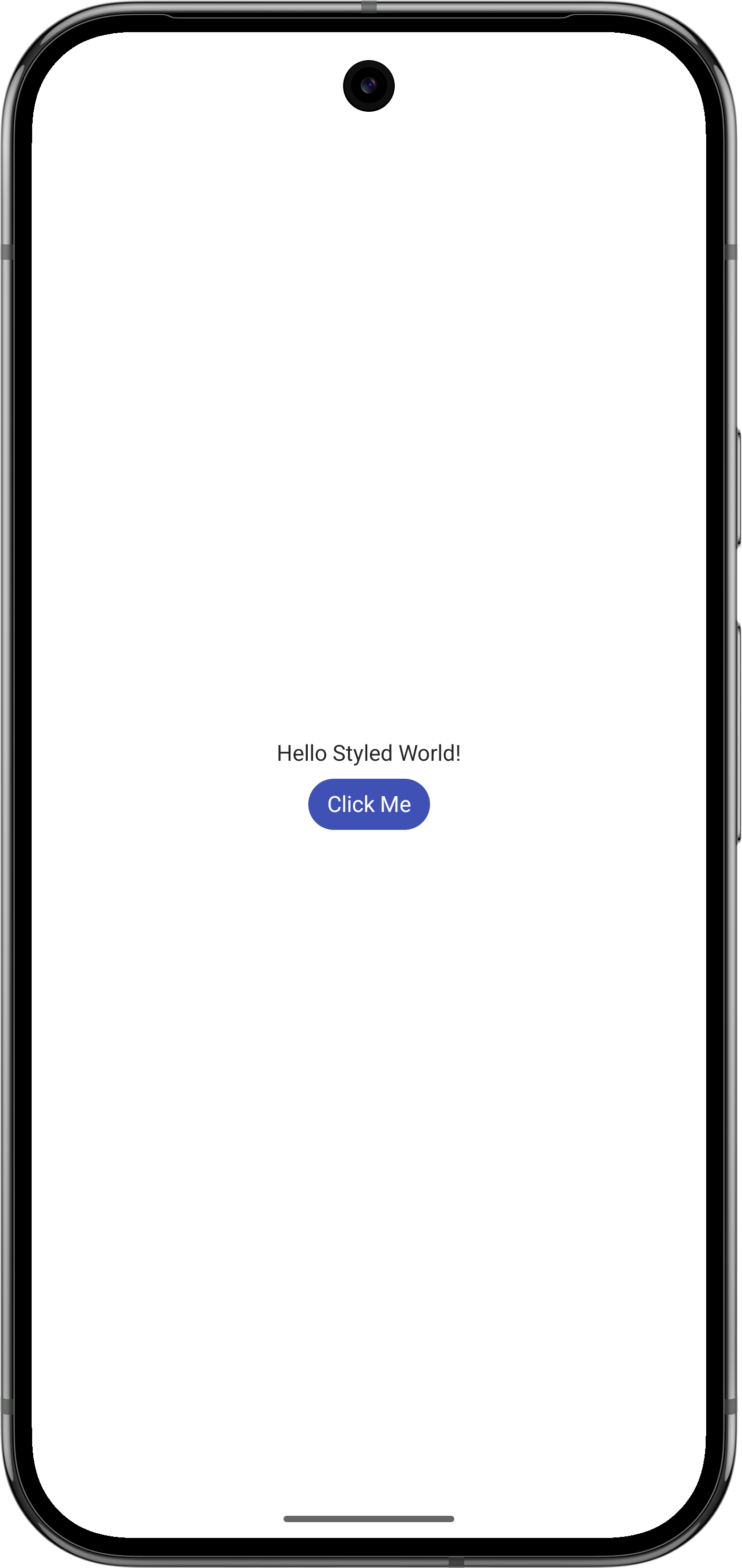
Brief explanation of the above code:
Theme[colors][background]returns thebackgroundtoken of thecolorsproperty. Similarly foronBackground,primaryandonPrimary.- The
ProvideContentColor()function forwards the givenColorto its children to render their contents with. - The
Textcomposable inherits the content color passed from theProvideContentColorand renders its text using theonBackgroundcolor of our theme. - We want our button to use the primary/onPrimary combo of the theme, so we use its
backgroundColorandcontentColorproperties.
That's it. Now whenever you update your colors in your XML theme, the changes will be reflected in your composables.
Use your XML dimens in Compose
Let's create some theme tokens for our spacing theme attributes, like we did for our colors:
val spacing = ThemeProperty<Dp>("spacing")
val small = ThemeToken<Dp>("small")
val medium = ThemeToken<Dp>("medium")
val large = ThemeToken<Dp>("large")
and now let's map them to our theme:
val AppTheme = buildTheme {
// get a reference to the calling (themed) context
val context = LocalContext.current
// map your XML colors to Compose
properties[colors] = mapOf(
background to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_background),
onBackground to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onBackground),
primary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_primary),
onPrimary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onPrimary),
)
// map your XML dimens to Compose
properties[spacing] = mapOf(
small to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_small),
medium to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_medium),
large to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_large),
)
}
We can now use our spacing inside our app, using Theme[spacing][small], Theme[spacing][medium] and
Theme[spacing][large].
For our example let's put some spacing between our elements using a Spacer:
@Composable
fun App() {
AppTheme {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Theme[colors][background]),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
ProvideContentColor(Theme[colors][onBackground]) {
Text("Hello Styled World!")
Spacer(Modifier.height(Theme[spacing][large]))
Button(
onClick = {},
backgroundColor = Theme[colors][primary],
contentColor = Theme[colors][onPrimary],
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 12.dp, vertical = 8.dp),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(100)
) {
Text("Click Me")
}
}
}
}
}
Use your XML typography in Compose
Let's create theme tokens for our text appearance attributes:
val typography = ThemeProperty<TextStyle>("typography")
val body = ThemeToken<TextStyle>("body")
Now we can map our XML text appearance to our theme tokens using resolveThemeTextAppearance:
val AppTheme = buildTheme {
// get a reference to the calling (themed) context
val context = LocalContext.current
// map your XML colors to Compose
properties[colors] = mapOf(
background to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_background),
onBackground to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onBackground),
primary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_primary),
onPrimary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onPrimary),
)
// map your XML dimens to Compose
properties[spacing] = mapOf(
small to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_small),
medium to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_medium),
large to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_large),
)
// map your XML typography to Compose
properties[textStyles] = mapOf(
body to resolveThemeTextAppearance(context, R.attr.textStyle_body),
)
}
Now you can use your XML typography in your composables using the new tokens and the ProvideTextStyle composable:
@Composable
fun App() {
AppTheme {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Theme[colors][background]),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
ProvideTextStyle(Theme[textStyles][body]) {
ProvideContentColor(Theme[colors][onBackground]) {
Text("Hello Styled World!")
Spacer(Modifier.height(Theme[spacing][large]))
Button(
onClick = {},
backgroundColor = Theme[colors][primary],
contentColor = Theme[colors][onPrimary],
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 12.dp, vertical = 8.dp),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(100)
) {
Text("Click Me")
}
}
}
}
}
}
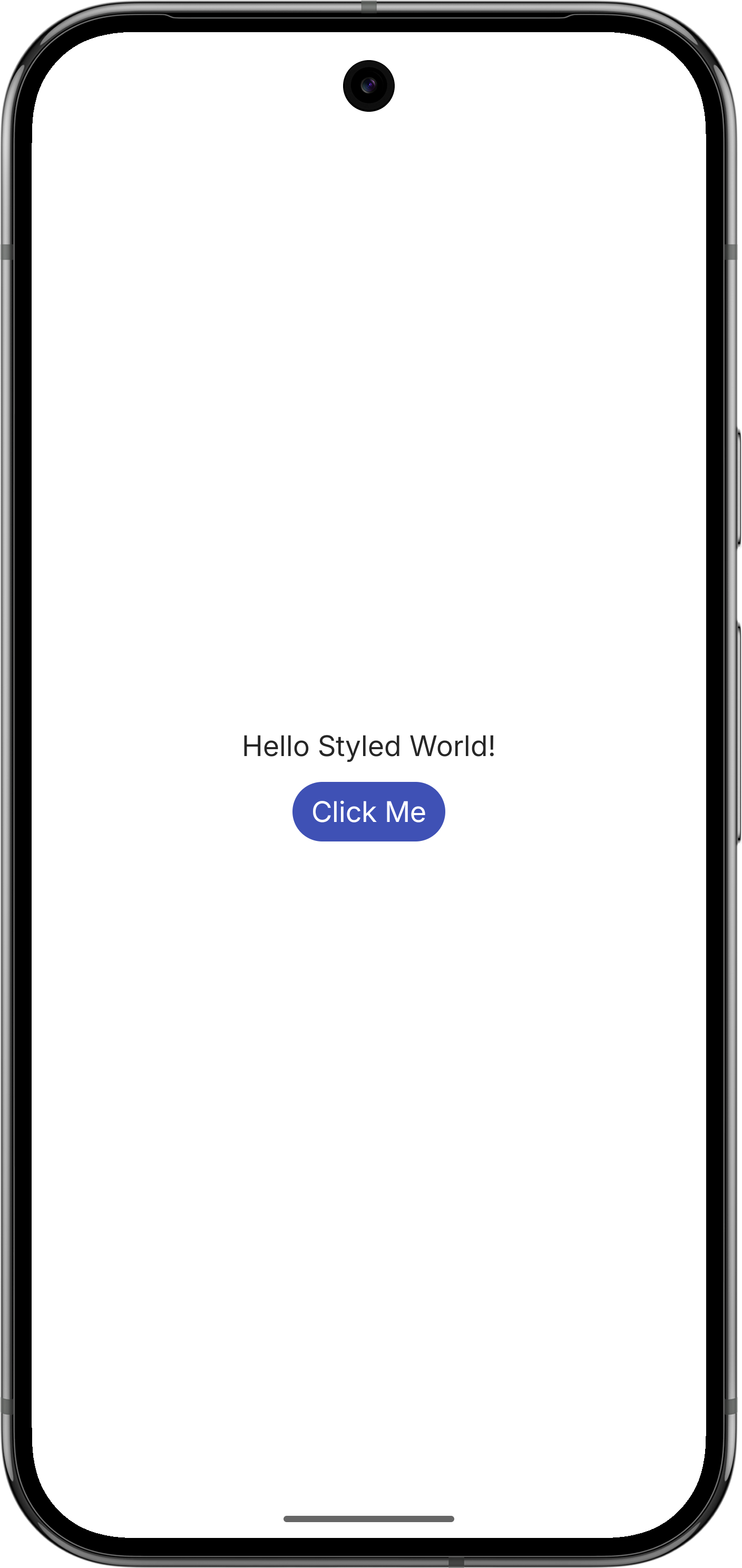
The resolveThemeTextAppearance function automatically resolves:
- Font size (
android:textSize) - Font family (
android:fontFamily) including custom fonts - Font weight and style (
android:textStyle) - Text color (
android:textColor) - Text shadows (
android:shadowColor,android:shadowDx,android:shadowDy,android:shadowRadius)
Use the Material Ripple effect in Compose
The Material ripple is a signature of Android apps, and we highly recommend using it in your apps for that polished touch effect.
For this, we provide a Compose Ripple Indication library:
// app/build.gradle.kts
implementation("com.composables:ripple-indication:1.0.0")
This introduces the rememberRippleIndication() function, that we can use in our compose theme:
val AppTheme = buildTheme {
// get a reference to the calling (themed) context
val context = LocalContext.current
// map your XML colors to Compose
val primary = resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_primary)
// create a ripple effect using the primary color
defaultIndication = rememberRippleIndication(
color = primary
)
properties[colors] = mapOf(
background to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_background),
onBackground to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onBackground),
primary to primary,
onPrimary to resolveThemeColor(context, R.attr.color_onPrimary),
)
// map your XML dimens to Compose
properties[spacing] = mapOf(
small to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_small),
medium to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_medium),
large to resolveThemeDp(context, R.attr.spacing_large),
)
// map your XML typography to Compose
properties[textStyles] = mapOf(
body to resolveThemeTextAppearance(context, R.attr.textStyle_body),
)
}
and rerun the app:
API Reference
resolveThemeColor
Returns a Color from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The attribute resource ID (@AttrRes) to resolve |
resolveThemeDp
Returns a Dp value from your XML theme dimensions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The dimension attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeSp
Returns a TextUnit value for text sizing from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The dimension attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemePx
Returns a Float pixel value from your XML theme dimensions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The dimension attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeInt
Returns an Int value from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The integer attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeFloat
Returns a Float value from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The float attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeString
Returns a String value from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The string attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeBoolean
Returns a Boolean value from your XML theme.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The boolean attribute resource ID to resolve |
resolveThemeTextAppearance
Returns a TextStyle with complete text styling including font size, family, weight, color, and shadows from your XML
TextAppearance.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
context | The Android Context to resolve attributes from |
resId | The TextAppearance style resource ID to resolve |